Plant oil extraction has undergone a remarkable transformation from ancient civilization practices to today’s sophisticated industrial processes. This journey spans over 5,000 years of human ingenuity, evolving from simple mechanical pressing techniques to advanced supercritical fluid extraction systems that preserve delicate bioactive compounds with unprecedented precision.
1. The Ancient Foundations: Traditional Oil Extraction Methods
Cold Pressing: The Timeless Technique
Cold pressing remains the gold standard for premium oil production, tracing its origins to 3000 BCE in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and India. This mechanical process operates below 50°C, preserving heat-sensitive nutrients and natural flavors that define high-quality oils.annamchekku
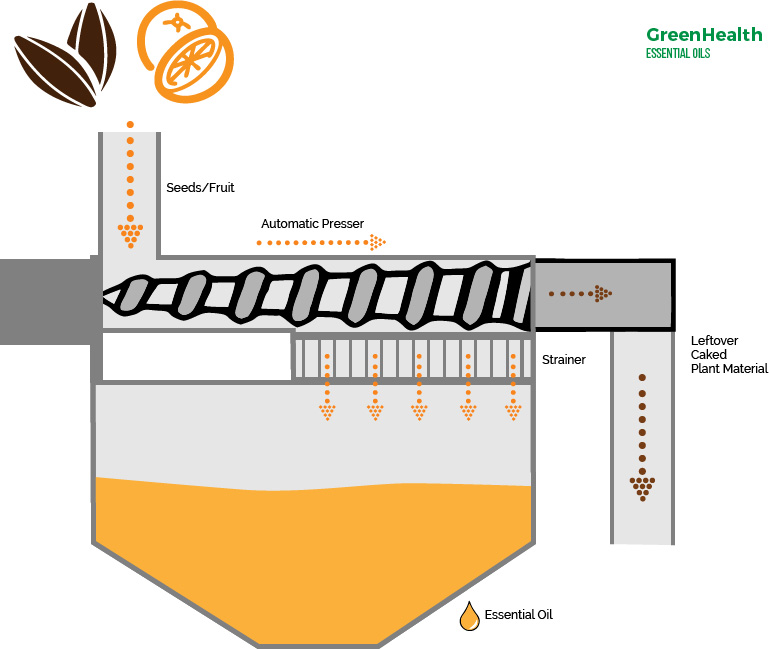
Traditional Process Steps:
- Seed Preparation: Oil-rich seeds are cleaned, dried, and sorted to remove impurities
- Grinding: Seeds are crushed using stone mills (Ghani), wooden presses (Chekku), or mortar and pestle systems
- Pressing: Mechanical pressure is applied without heat to extract oil from cellular structures
- Separation: Oil is separated from pulp through natural gravity sedimentation
- Filtration: Basic straining removes remaining solid particlesstandardcoldpressedoil
In India, the traditional ‘Chekku’ (wooden press), ‘Ghani’ (stone mill), and ‘Kolhu’ (bullock-driven press) were integral to village life. These slow, natural processes ensured oils retained their nutrients, aroma, and medicinal properties, yielding approximately 70-85% of available oil content.nuft+1
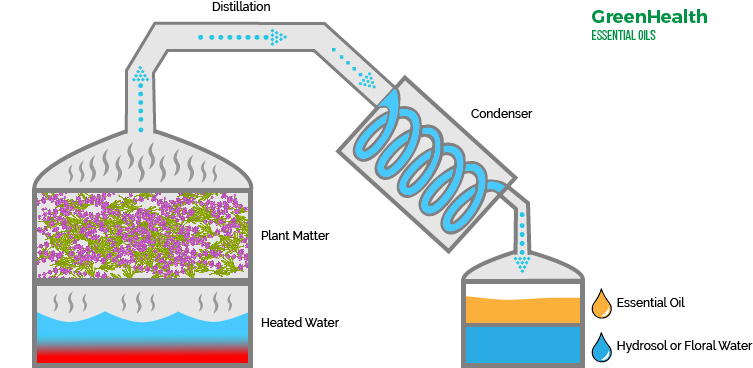
Steam and Water Distillation: Aromatic Oil Extraction Mastery
Steam distillation, refined during the Arabian Golden Age (8th-9th centuries), became the primary method for extracting essential oils from aromatic plants. This process involves:
- Plant material placement on perforated grids above boiling water
- Steam penetration through plant tissues, rupturing oil-bearing cells
- Vapor condensation separating essential oils from aromatic water (hydrosol)
- Natural separation based on density differencesagritech.tnau
Water distillation completely immerses plant material in boiling water, making it ideal for delicate flowers like roses and orange blossoms that would clump together under direct steam.agritech.tnau
Enfleurage: The Art of Fat Absorption
Enfleurage represents one of history’s most elegant extraction methods, originating in 9th-century Persia and reaching perfection in 19th-century Grasse, France. This technique leverages fat’s natural ability to absorb aromatic compounds:scentspiracy
Cold Enfleurage Process:
- Flower layering: Fresh petals (jasmine, tuberose, gardenia) are placed on glass sheets coated with odorless fat
- Repeated cycles: Process repeats 30-40 times until fat becomes saturated with fragrance
- Alcohol extraction: Pomade is washed with ethanol to extract pure absolutescentspiracy
Though labor-intensive and requiring 30-100 grams of flowers per frame, enfleurage produces ultra-premium quality oils with unmatched olfactory complexity.
2. Industrial Oil Extraction Revolution: Mechanization and Scale
Hot Pressing and Expeller Technology
The 20th century brought mechanized expeller pressing, combining traditional principles with industrial efficiency. Hot pressing operates at 80-120°C, increasing yield to 85-95% but potentially compromising some heat-sensitive compounds.standardcoldpressedoil
Modern expeller systems feature:
- Continuous screw mechanisms for automated operation
- Temperature and pressure control for optimal extraction
- Higher throughput capacity processing hundreds of tons daily
- Reduced manual labor requirementsandersonintl
Solvent Extraction: Chemical Efficiency
Hexane extraction, developed in the 1940s, revolutionized large-scale oil production by achieving 95-99% extraction efficiency. This industrial process involves:andersonintl
Five-Step Solvent Process:
- Pre-pressing: Initial mechanical extraction removes 85-89% of oil
- Solvent treatment: Hexane dissolves remaining oil from seed cake
- Miscella separation: Oil-solvent mixture is separated from solid residue
- Solvent recovery: Distillation removes hexane for reuse (99.9% recovery)
- Oil refining: Final purification produces commercial-grade oilbestoilpressmachines
Hexane advantages include:
- High oil solubility at relatively low temperatures
- Low boiling point (69°C) enabling easy removal
- Chemical stability under process conditions
- Water immiscibility facilitating separationkumarmetal
However, environmental concerns about hexane’s classification as a hazardous air pollutant under the Clean Air Act 1990 have driven research into alternative solvents.onlinelibrary.wiley

3. Modern Innovation in Oil Extraction: Precision and Sustainability
Supercritical CO2 Extraction: The Premium Standard
Supercritical fluid extraction using carbon dioxide (SFE-CO2) represents the pinnacle of modern extraction technology, offering unprecedented selectivity and purity. Operating above CO2’s critical point (31.1°C and 73.8 bar), this method provides:pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Key Advantages:
- Solvent-free operation: CO2 leaves no residue after pressure release
- Temperature control: Low-temperature operation preserves heat-sensitive compounds
- Selective extraction: Precise parameter control targets specific compounds
- Environmental safety: Non-toxic, non-flammable, recyclable solvent
- FDA approval: Unrestricted use in food applicationspmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Typical Operating Parameters:
- Pressure: 150-300 bar
- Temperature: 40-80°C
- Extraction time: 2-6 hours
- CO2 flow rate: 120 g/min
- Yield: 90-99% depending on materialpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Research shows SFE-CO2 proved superior for four out of six plant materials, particularly seeds with lower oil content, while achieving higher phytosterol concentrations and antioxidant activity.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih

Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction: Acoustic Enhancement
Ultrasonic extraction, developed in the 1990s, uses acoustic cavitation to rupture plant cell walls, facilitating oil release. Operating at 20-100 kHz frequencies, this method:
- Reduces extraction time to 30-120 minutes
- Operates at lower temperatures (40-60°C) preserving quality
- Increases yields by 10-25% compared to conventional methods
- Minimizes solvent requirements for environmental benefitpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Mechanism: Ultrasonic waves create microscopic cavitation bubbles that collapse violently, generating localized high pressures and temperatures that disrupt cellular structures without bulk heating.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Microwave-Assisted Extraction: Rapid Processing
Microwave technology accelerates extraction through selective heating of polar molecules in plant tissues. This modern technique offers:
- Ultra-fast processing: 5-30 minutes extraction time
- Energy efficiency: Direct internal heating reduces overall energy consumption
- Improved yields: 80-95% extraction efficiency
- Quality preservation: Rapid processing minimizes thermal degradationpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Microwave-assisted extraction works by heating moisture within plant cells, creating internal pressure that ruptures cell walls and facilitates oil release more efficiently than external heating methods.
Enzyme-Assisted Extraction: Biological Precision
Enzymatic extraction employs specific enzymes (cellulases, pectinases, proteases) to break down plant cell walls at the molecular level. This biotechnological approach provides:
- Mild conditions: 40-60°C operation preserves delicate compounds
- High selectivity: Enzymes target specific cellular components
- Improved yields: 80-92% efficiency through complete cell wall degradation
- Reduced processing time: 2-8 hours versus days for traditional methodsagriwaysjournal
4. Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs Modern Methods
Quality and Nutrient Retention
Traditional methods excel in preserving natural characteristics but show variable results:
- Nutrient retention: 80-90% of original compounds preserved
- Flavor profile: Authentic, unaltered taste and aroma
- Processing integrity: Minimal chemical or thermal stress
- Shelf stability: Shorter due to natural oxidation processesgreenskybio

Modern methods achieve superior consistency and preservation:
- Nutrient retention: 95-99% through controlled conditions
- Standardization: Consistent quality across batches
- Extended shelf life: Advanced preservation techniques
- Bioactive enhancement: Selective extraction of beneficial compoundspmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Economic and Environmental Considerations
Traditional extraction offers sustainability advantages:
- Low energy consumption: Solar drying, manual/animal power
- Minimal environmental impact: No chemical solvents or emissions
- Local employment: High manual labor requirements support communities
- Low capital investment: Simple equipment and infrastructuregreenskybio
Modern methods provide industrial efficiency:
- High scalability: Process thousands of tons daily
- Automated operation: Reduced labor costs and human error
- Optimized yields: Maximum oil recovery from raw materials
- Quality control: Precise monitoring and standardization systemsandersonintl
Future Innovations and Trends
Emerging technologies combine traditional wisdom with modern innovation:
Green Solvents: Vegetable oils as extraction solvents offer biodegradable, non-toxic alternatives to hexane, particularly effective for carotenoid extraction with yields comparable to conventional methods.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Hybrid Methods: Combining ultrasound with supercritical CO2 or microwave with enzymatic treatment optimizes both efficiency and quality.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Nanotechnology Integration: Nanoparticle enhancement improves extraction efficiency and enables targeted compound isolation.idol
Artificial Intelligence: Machine learning optimization of extraction parameters maximizes yield while preserving quality characteristics.vocal
5. Choosing the Right Method in Your Oil Extraction
Premium Quality Oils:
- Cold pressing: High-oil content seeds (olive, avocado, nuts)
- Supercritical CO2: Heat-sensitive compounds, pharmaceutical applications
- Enfleurage: Ultra-premium fragrance oils, luxury cosmetics
Commercial Production:
- Solvent extraction: Large-scale processing, maximum yield requirements
- Hot pressing: Balance of efficiency and quality for food oils
- Steam distillation: Essential oils for aromatherapy and flavoring
Specialty Applications:
- Ultrasound-assisted: Research and development, small-batch production
- Microwave extraction: Rapid processing needs, laboratory scale
- Enzyme-assisted: Difficult extractions, biotechnology applications
6. Conclusion: Bridging Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science
The evolution of plant oil extraction demonstrates humanity’s persistent quest for efficiency while preserving quality. Traditional methods established the foundation of understanding how to extract oils while maintaining their beneficial properties, creating techniques that remain valuable today for premium applications.
Modern innovations have not replaced traditional methods but rather expanded our capabilities, offering solutions for different scales, qualities, and applications. The future lies in intelligent integration of both approaches – leveraging traditional wisdom for quality insights while applying modern technology for precision, efficiency, and sustainability.
As consumer demand grows for both high-quality artisanal oils and sustainable industrial production, the plant oil extraction industry continues evolving, combining the best of ancient practices with cutting-edge innovation to meet diverse global needs while protecting environmental and human health.
This synthesis of traditional and modern approaches ensures that whether producing small-batch, cold-pressed olive oil or large-scale, supercritical CO2-extracted specialty compounds, extraction methods can be tailored to achieve optimal results for specific applications, market requirements, and sustainability goals.
About us
Try it for yourself. Freshdi.com
Global Agri B2B Marketplace.