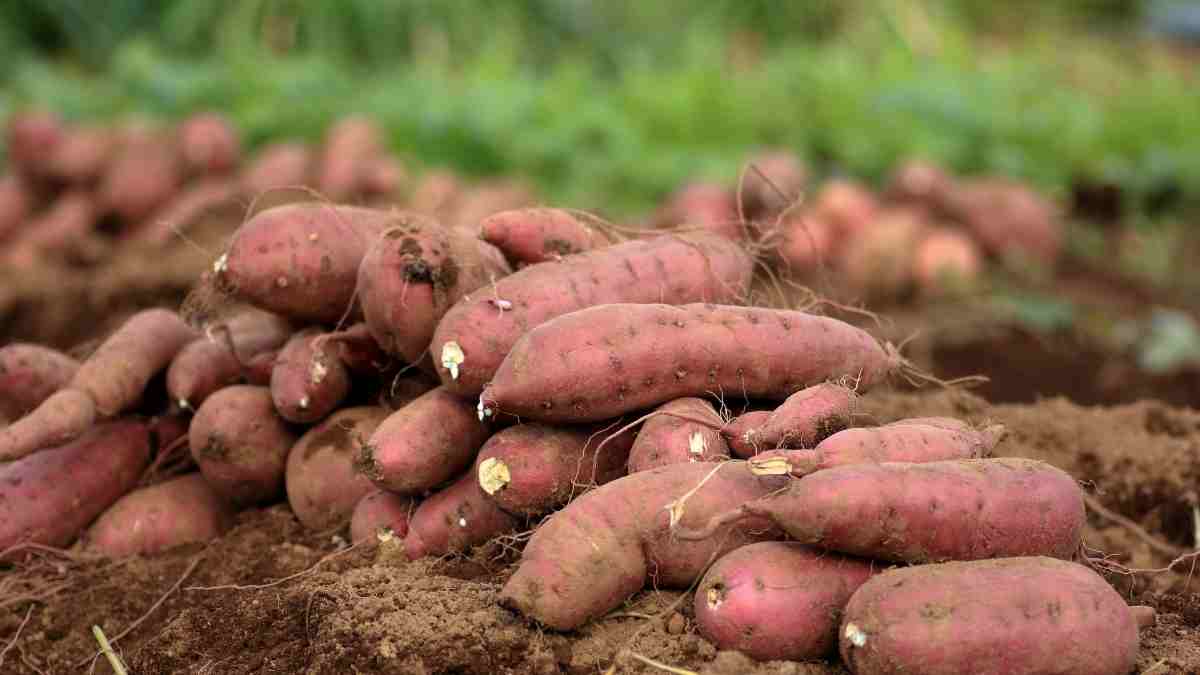
Sweet potatoes have emerged as one of the world’s most valuable crops, with global production reaching 102.34 billion kilograms in 2023 and China alone contributing 51.40 billion kg (55.1% of world production). The global sweet potato market, valued at $314.5 billion in 2024, is projected to reach $413.9 billion by 2031 with a steady 4.0% CAGR.
Global Sweet Potato Market: Opportunities and Trends
Production Sweet Potato and Market Leaders
China dominates global sweet potato production with 55.1% market share, but emerging players are reshaping the landscape. Egypt’s remarkable growth exemplifies this trend – Egyptian sweet potato exports to Europe jumped from 35,224 MT in 2020 to 149,551 MT in 2024, valued at $113 million. This surge reflects strategic advantages including geographic proximity to European markets and counter-seasonal production that fills supply gaps when other exporters are offline.
Malawi (8.62% market share), Tanzania (4.84%), and Nigeria (4.38%) round out the top five producers, indicating Africa’s growing importance in global sweet potato markets.

Sweet Potato by Market Segmentation and Consumer Preferences
The sweet potato industry encompasses diverse market segments:
By Variety: Hannah, Japanese, Jewel, Stokes Purple, and Garnet varieties each target specific consumer preferences and culinary applications.
By Form: Whole products dominate (85% market share), followed by paste, flour, and processed forms.
By Application: Food applications lead (78%), with beverages (15%) and animal feed (7%) representing growth sectors.
Regional Growth Projections show Asia-Pacific markets expanding fastest, driven by rising disposable incomes and health consciousness. North American and European markets focus on premium organic and specialty varieties, commanding higher prices for quality-focused producers.
Sweet Potato Varieties: Choosing the Right Cultivars
Orange-Fleshed Varieties: The Market Standards
‘Beauregard’ remains the most popular orange-fleshed variety in the United States, prized for its high yields, excellent storage characteristics, and sweet flavor. Research shows Beauregard plants produce almost 2X the biomass of purple varieties, with individual roots averaging 1.5X wider than purple alternatives.
‘Covington’ (light rose skin) offers improved disease resistance, particularly against root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita race 3), making it valuable for sustainable production systems.

‘Jewel’ (orange skin and flesh) provides exceptional beta-carotene content – up to 922 mcg RAE per medium sweet potato, delivering 213% of daily vitamin A requirements.
Purple-Fleshed Varieties: The Antioxidant Champions
Purple sweet potatoes contain 18 high-confidence anthocyanin derivatives with acylated peonidin and cyanidin compounds contributing to >90% of total anthocyanin signal. These compounds provide superior antioxidant capacity compared to orange varieties.
‘Purple Splendor’ (NC State University release, 2021) offers uniform, blocky to round elliptic shapes with high No.1 root packout and excellent storage characteristics.
‘All Purple’, ‘Kotobuki’, and ‘Purple Passion’ each deliver ~800 mg anthocyanins per 100g dry weight, making them valuable for health-focused markets and functional food applications.
‘Stokes Purple’ features deep purple skin and flesh with creamy texture when cooked, appealing to gourmet and specialty markets willing to pay premium prices.
Specialty and Regional Varieties
‘Okinawa’ (Japanese variety) provides exceptional longevity benefits – populations consuming traditional Okinawan diets including purple sweet potatoes show remarkable health outcomes.
‘Hannah’ offers cream-colored flesh with lower sweetness than orange varieties, suitable for savory applications and consumers preferring less sweet options.
‘Molokai Purple’ combines purple skin with dark purple interior, creating striking visual appeal for premium restaurant and retail applications.
Soil Preparation and Site Selection
Optimal Soil Conditions
Sweet potatoes thrive in well-drained, sandy loam soils with pH between 5.8-6.2. Soil temperature must reach minimum 60°F (15.5°C) at 4-inch depth before planting to ensure successful establishment.
Deep soil preparation is critical – sweet potato roots can penetrate 3-5 feet deep while vines spread 10-15 feet horizontally. Create raised beds 8-10 inches high to improve drainage and soil warming, particularly important in cooler climates.
Fertility Management
Sweet potatoes are heavy feeders requiring strategic nutrient management:
Pre-plant application: 60-80 lbs nitrogen, 60-100 lbs phosphorus, and 120-160 lbs potassium per acre based on soil testing.
Organic matter: Incorporate 2-4 inches of well-composted organic matter to improve soil structure and water retention.
Micronutrients: Ensure adequate boron and magnesium availability – deficiencies cause cracking and poor root development.
Avoid excessive nitrogen which promotes vine growth at expense of root development. Split nitrogen applications with 1/3 at planting and 2/3 at layby (30-40 days after planting).

Planting Strategies and Spacing
Slip Production and Selection
High-quality slips form the foundation of successful sweet potato production. Select disease-free seed roots and maintain bed temperatures 75-85°F for optimal slip development.
Slip characteristics for transplanting:
- 6-9 inches tall with 4-6 leaves
- Pencil-thick stems indicating good root development potential
- Disease-free appearance with vibrant green foliage
- Well-developed root systems when gently pulled from beds
Field Planting Specifications
Row spacing: 42-48 inches between rows for mechanical cultivation
Plant spacing: 12-15 inches within rows (12,000-15,000 plants per acre)
Planting depth: Set slips with root zone 3-4 inches deep and 2-3 nodes above soil surface
Timing: Plant after soil temperature reaches 65°F consistently and frost danger passes (typically late May-early June in temperate zones)extension.uga
Integrated Pest Management
Major Disease Challenges
Sweet Potato Virus Disease (SPVD) represents the most serious threat globally, caused by synergistic interaction between sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus (SPCSV) and sweet potato feathery mottle virus (SPFMV). This combination can cause 56-98% yield losses.
Prevention strategies:
- Use certified virus-free planting material
- Control aphid vectors through integrated management
- Remove infected plants immediately to prevent spread
- Implement 2-year rotations away from sweet potato family crops
Fungal Disease Management
Fusarium root rot (Fusarium oxysporum, F. solani) causes dark tan rot with sharp demarcation between healthy and diseased tissue. Stem infections appear as swollen areas with internal vascular discoloration.
Management approaches:
- 2-year crop rotations with non-host crops
- Soil fumigation in severely infested fields
- Resistant varieties like ‘Covington’ and ‘Evangeline’
Black rot (Ceratocystis fimbriata) creates irregular sunken spots, dark brown to black with characteristic black dots containing fungal spores. Proper curing (85-90°F, 85% humidity for 4-7 days) helps prevent infection during storage.

Nematode Control Strategies
Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita) cause galling and yield reduction in susceptible varieties. Southern root-knot nematode (M. incognita race 3) is particularly problematic in southeastern United States.
Integrated management:
- Resistant varieties: ‘Covington’, ‘Bonita’, ‘Evangeline’ show strong resistance
- Crop rotation: Peanuts serve as non-hosts, breaking nematode cycles
- Cover crops: Rye, mustard, and radishes help suppress populations
- Soil fumigation: Pre-plant applications in heavily infested fields
Insect Pest Management
Sweet potato weevil (Cylas formicarius elegantulus) poses the greatest threat in warmer regions. Adults lay eggs in exposed roots, with larvae tunneling through storage roots.
Control measures:
- Plant beds located >1 mile from previous year’s fields
- Weekly foliar insecticide applications during growing season
- Pheromone traps for monitoring adult populations
- Prompt harvest and destruction of crop residues
Wireworms and white grubs damage roots through feeding tunnels. Pre-plant soil insecticides provide 4-6 weeks protection, followed by layby applications to maintain control.
Water Management and Irrigation
Critical Growth Periods
Sweet potatoes require consistent moisture but are sensitive to waterlogged conditions. Most critical periods for irrigation include:
Establishment phase (0-3 weeks): 1-1.5 inches weekly to ensure slip survival and root establishment
Root development (4-8 weeks): 1 inch weekly with deep, infrequent applications encouraging root penetration
Root bulking (9-15 weeks): 0.75-1 inch weekly avoiding excess moisture that promotes splitting
Irrigation System Selection
Drip irrigation provides optimal water management with reduced disease pressure compared to overhead systems. Plastic mulch combined with drip irrigation offers additional benefits:
- Soil temperature increase of 5-8°F accelerating growth
- Weed suppression reducing competition
- Moisture conservation improving water use efficiency
- Earlier harvest by 7-14 days in northern climates
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Management
Harvest Timing and Techniques
Harvest indicators:
- Root diameter reaches marketable size (2-3.5 inches)
- Soil temperature drops below 55°F triggering harvest urgency
- 120-140 days after planting depending on variety
- Vines begin yellowing naturally in fall
Mechanical harvesting requires proper equipment adjustment to minimize damage. Digging depth should extend 6-8 inches below ridge top to avoid cutting roots.
Curing and Storage Protocols
Curing process (first 7-10 days):
- Temperature: 85-90°F
- Humidity: 85-90%
- Ventilation: Adequate airflow preventing condensation
- Purpose: Heal wounds, develop protective skin
Long-term storage (after curing):
- Temperature: 55-60°F
- Humidity: 85-90%
- Duration: 6-12 months depending on variety
- Monitoring: Regular inspection removing deteriorating roots
Nutritional Value and Health Benefits
Exceptional Nutrient Density
Sweet potatoes rank among the most nutritious vegetables available. One cup (200g) baked sweet potato provides:
- Vitamin A: 213% DV (primarily as beta-carotene)
- Vitamin C: 44% DV supporting immune function
- Manganese: 43% DV for enzyme function
- Potassium: 20% DV for cardiovascular health
- Fiber: 6.6g supporting digestive health
Purple varieties offer additional benefits through anthocyanin compounds providing:
- Superior antioxidant capacity compared to orange varieties
- Anti-inflammatory effects reducing chronic disease risk
- Cognitive support through neuroprotective compounds
- Cardiovascular benefits improving endothelial function
Functional Food Applications
Research demonstrates sweet potatoes’ potential for managing metabolic disorders:
Blood sugar regulation: Purple sweet potato extracts help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose spikes
Weight management: High fiber and resistant starch content promote satiety while supporting healthy gut bacteria
Eye health: Beta-carotene content prevents vitamin A deficiency and supports visual function, particularly important in developing countries
Future Market Opportunities
Emerging Processing Applications
The sweet potato processing market shows strong growth potential with applications expanding beyond traditional uses:
Functional ingredients: Sweet potato flour, purees, and concentrates finding applications in bakery, confectionery, and beverage industries
Health products: Anthocyanin-rich extracts from purple varieties targeting nutraceutical and supplement markets
Pet food: Sweet potato-based pet foods capitalizing on natural, nutritious ingredient trends
Sustainable Production Systems
Organic certification commands premium prices with consumer willingness to pay 15-25% more for certified organic sweet potatoes. Integrated pest management and biological control agents like Trichoderma harzianum offer sustainable alternatives to chemical inputs.
Climate resilience makes sweet potatoes valuable for climate change adaptation. Their drought tolerance and heat stress resistance position them well for expanding production into marginal agricultural areas.
Conclusion: Sweet Potato Success Strategies
Sweet potato cultivation represents an exceptional opportunity combining strong market demand, nutritional benefits, and agricultural sustainability. With global markets valued at $314.5 billion and growing at 4.0% annually, well-managed sweet potato operations can achieve excellent profitability.
Key success factors include:
- Variety selection matching market demands and growing conditions
- Soil preparation ensuring optimal drainage and fertility
- Integrated pest management preventing major disease and insect losses
- Water management supporting consistent root development
- Post-harvest handling maintaining quality through proper curing and storage
Market opportunities continue expanding, particularly for specialty varieties, organic production, and value-added processing. Egyptian producers demonstrate how strategic positioning can capture premium export markets, while purple varieties offer functional food applications commanding higher prices.
Whether targeting local farmers markets with specialty varieties or global export opportunities with standard cultivars, sweet potatoes offer reliable returns for growers implementing best management practices. The combination of proven cultivation techniques, diverse market applications, and growing health consciousness ensures sweet potatoes will remain valuable crops for years to come.
By following these comprehensive guidelines while staying informed about evolving market trends and consumer preferences, sweet potato growers can build sustainable, profitable operations that capitalize on this remarkable crop’s continued growth trajectory.
About us
Try it for yourself. Freshdi.com
Global B2B Marketplace.